This Wizard will guide you via simple steps to help you to re-assemble a damaged or disassembled RAID set to create a Virtual Disk Array. It will allow you to review and recover data located on the RAID set.
To run this Wizard - click Create Virtual Array from the Wizards menu, or click Create Virtual RAID button in Tools Tab of Command Bar.
Select a RAID type to be reconstructed:
Choose disks to compose a Virtual Disk Array.
Use the [Damaged Disk] virtual device instead of the disk that is physically damaged (e.g. a non spinning disk), or is known to contains invalid information. Some RAIDs types (Mirror, RAID5) allow you to recover information even if one of the disks is lost this way.
Choose default geometry options or specify custom values.
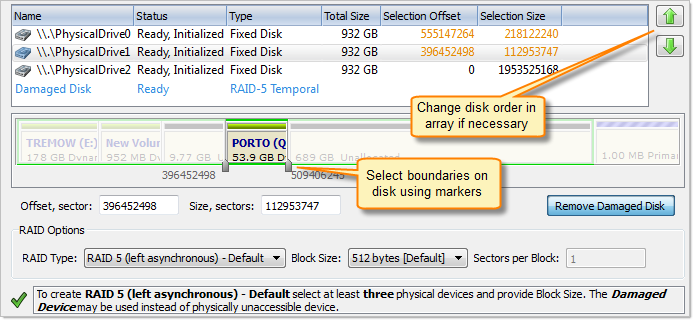
Arrange disks in the Virtual Disk Array using the Up and Down buttons. If you do not know the particular disk order, try all possible configurations: write down the current order, assemble the array and check the data in it. If the data is not accessible - try a different order until one works.
Some RAID types (Span, RAID5) require a certain stripe block size, thus you will need to specify it in Options box. If you are not sure of this value, you may try to find it in the Controller's configuration utility (Controller's BIOS), or you can try different block sizes and check the results. The most commonly used values are: 32kb, 64kb, 128kb.
Review and confirm parameters for the Virtual Disk Array to be created.
Click the Create button to create the Virtual Disk Array.
Click the Finish button to close the Wizard if the RAID was reconstructed successfully, otherwise you will see error messages.
A New Data Storage Device and one or several drives (if detected) will appear in the list of devices and drives in the Recovery Explorer.
You can work with reconstructed RAID sets the same way as you work with a regular storage device or logical drive, i.e. scan device for deleted/damaged partitions, scan drives and search for files, recover/copy files and folders to another safe location, etc...